This article performance improvement practices when building pivot reports. The value of following these practices will improve the performance of data retrieval from the Data Wearhouse and allow for higher data capacity and faster retr
Pivot Table Performance
Practical Example
Slicer Performance
Pivot Tables
Filters:-
- Filtering on large attribute lists such as “Style Code” will cause performance issues.
- When we exclude a single field from a large list, such as style code, T
This will cause the query that is run to search against all filters and attributes to every style code individually that is not filtered out.
This causes the system to repetitively run through the same data causing inefficiencies and bloat the query.
- Where it would have run once it is now run all non-filtered Items* Attribute1,2,3 *Calculation1,2,3 to make sure that it should not be excluded from the query.
Improvement Practice
- Do not filter on long large lists, instead apply filters that can filter out unwanted data from the list.
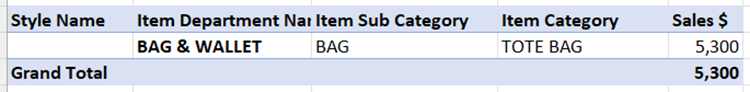
Instead of filtering on “Style Code” Filter on Product – Department to exclude unwanted data
In the below example, we can see that instead of filtering on all style names, we could instead filter on the 20-30 Item Categories.
(It is important to note that this could also be a candidate for exclusion or flag.
Flags are valuable when you do not want to permanently exclude items but it is helpful to toggle between data E.G -The Flag “IS Member” we would not want to filter out half the users when trying to identify member sales, as such we use an attribute “member” and create a flag that sorts out all unwanted data.
Thought Experiment – The Coin Example – A person gives you 20, 20c coins.
Unfiltered Pivot – The Person asks (How many coins are you holding)
- “20” (it's quick as it doesn’t require any checks, count all)
Filtered on an attribute – The Person asks, (How many coins have the year 2000 on them)
- We need to check each coin ONCE to see if it matches 2000. (Still quick, but requires a bit more time)
Filtered on multiple attributes – The Person asks, (How many coins have 1980,1981,1982...1992,2000)
- We need to check each coin, against all 20 years to see if it matches any of the years outlined in the list. (This is really slow as you must check every coin against 20 records to make sure it matches a date)
Flagged Attributes – The Parson asks, (How many coins have 1980,1981,1982...1992,2000)
tRS has come in and painted all coins that have the year 1980-2000 RED.
• You just need to count the red coins (it's really quick again)
Slicers
Slicer Settings:-
Similarly to filters, Slicers have a hidden setting that improves the visual aspect of a slicer whilst impacting performance, by filtering out items with no data (Filtering on multiple attributes).- When we Hide Items with no data, the same query is run requiring the search request to validate against every attribute that is not filtered out to confirm it is in the list.
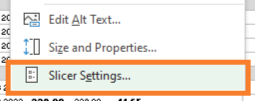
To Improve this we need to turn off the slicer's default option, in the slicer settings.
To access the slicer settings,
• Right-click on the slicer
• Select Slicer Settings